Introduction to Carbon Footprint Measurement
Definition of a carbon footprint
A carbon footprint is the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs) emitted directly or indirectly by an entity, such as a person, product, or business. This comprehensive carbon footprint measurement accounts for the impact of activities on the environment and climate change, encompassing emissions from carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and other greenhouse gases.
Understanding and accurately calculating a carbon footprint is crucial for fostering environmental awareness and accountability, allowing individuals and organizations to identify significant sources of emissions and target them for reduction. Typically expressed in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e), a carbon footprint measurement helps quantify the environmental impact and guides efforts towards sustainable practices by highlighting how to reduce carbon footprint effectively.
Importance of Measuring Carbon Footprint
Measuring your carbon footprint is essential for several reasons. It helps you understand and take responsibility for your greenhouse gas emissions, promoting environmental awareness and personal accountability. By identifying major sources of emissions, you can set realistic goals for reduction and track progress over time.
For businesses, measuring the carbon footprint can provide a competitive advantage by enhancing brand reputation, attracting sustainability-conscious customers, and potentially leading to economic savings. Accurate measurement also facilitates compliance with environmental regulations and standards, ensuring transparency and trust with stakeholders.
Examples of Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint can refer to the impact of an individual, company, event, or product throughout its lifecycle. For instance, the carbon footprint of an individual includes emissions from daily activities such as commuting, energy use at home, and dietary choices. For businesses, it encompasses operational emissions, including energy consumption, transportation, and waste management. Events like music festivals or sporting events also have significant carbon footprints due to the large number of participants and associated activities.
Additionally, the carbon footprint of a product considers the emissions from raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, usage, and disposal, providing a comprehensive view of its environmental impact.
Understanding Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Types of greenhouse gas emissions
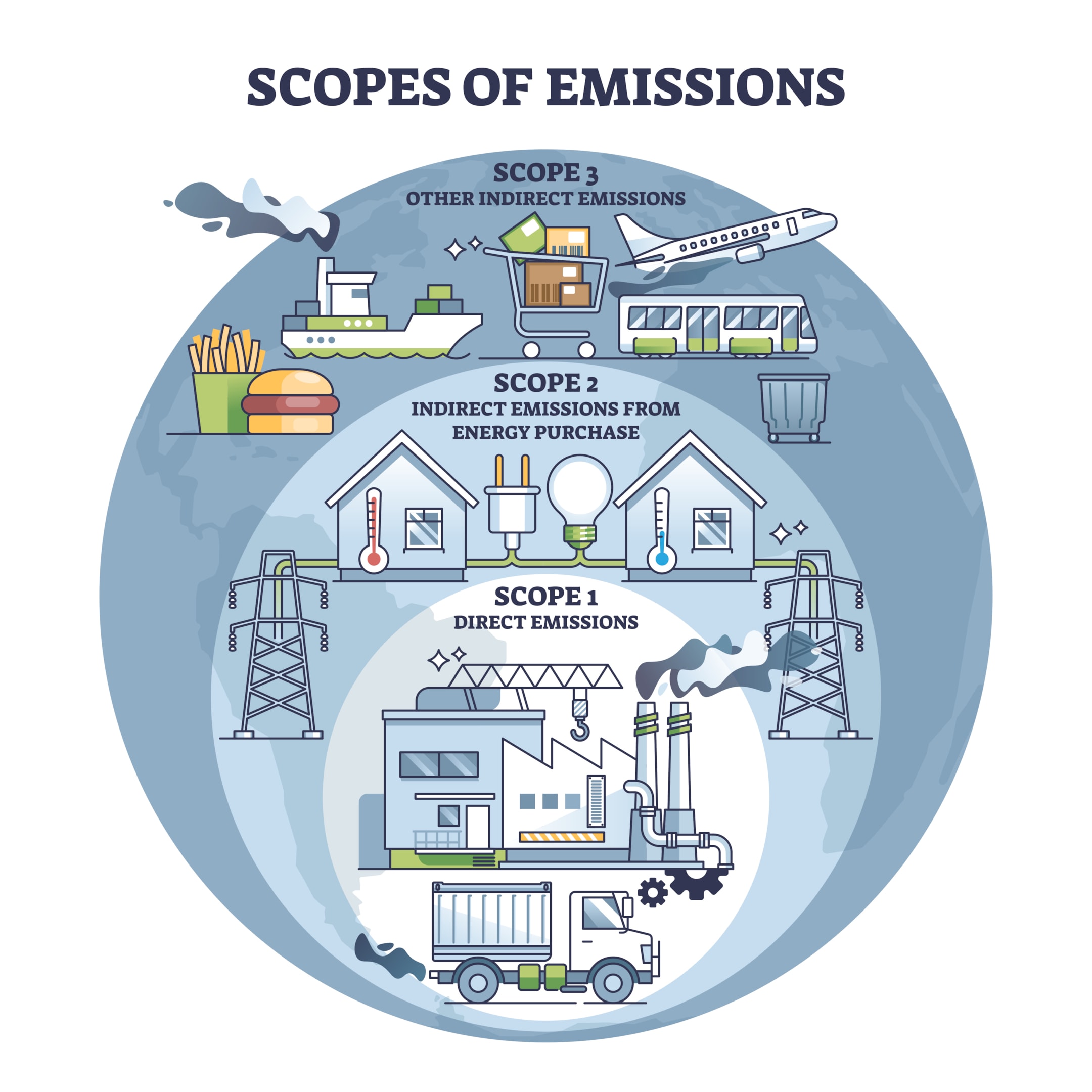
Greenhouse gas emissions are categorized into three scopes by the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, providing a standard framework for measuring and reporting emissions. Scope 1 emissions refer to direct emissions that originate from sources that are owned or controlled by the organization, including activities like on-site fuel combustion.
Scope 2 emissions are indirect emissions from the consumption of purchased electricity, heat, or steam. Scope 3 emissions encompass all other indirect emissions that occur in the value chain, including those from the production of purchased goods and services, business travel, and waste disposal. This classification helps organizations comprehensively assess their total full chain emissions, and identify opportunities for reduction across their operations.
Direct Carbon Emissions (Scope 1)
Direct or Scope 1 carbon emissions originate from sources that are directly owned or controlled by the entity. These include emissions from on-site fuel combustion, such as those produced by boilers, furnaces, and company vehicles. For instance, a factory that burns natural gas for heating or a fleet of delivery trucks using diesel fuel generates direct emissions.
By understanding and managing Scope 1 emissions, organizations can implement targeted strategies to reduce their direct environmental impact, such as optimizing fuel use, switching to cleaner energy sources, and enhancing operational efficiency.
Indirect Carbon Emissions (Scope 2 and 3)
Indirect carbon emissions are those that occur outside the direct control of the organization but are a consequence of its activities. Scope 2 emissions are associated with the consumption of purchased electricity, heat, or steam, while Scope 3 emissions cover a broad range of indirect activities, including upstream and downstream processes. Examples of Scope 3 emissions include the production and transportation of raw materials, employee commuting, business travel, and the disposal of waste.
Understanding and managing these emissions is crucial for a comprehensive carbon footprint assessment, enabling organizations to engage with suppliers, optimize their supply chains, and promote sustainable practices throughout their operations.
Why Measure Your Carbon Footprint?
Corporate commitment and competitive advantage
Measuring and reducing carbon emissions demonstrates a company’s commitment to environmental sustainability, enhancing its reputation among customers, stakeholders, and investors. This proactive approach can lead to improved brand loyalty, increased customer satisfaction, and a competitive edge in the market.
Companies that prioritize environmental management and sustainability are often viewed more favorably, attracting eco-conscious consumers and partners. Additionally, setting and achieving carbon reduction goals can position a business as a leader in its industry, fostering a positive corporate image and driving long-term success.
Demand from Customers and Suppliers
Customers and suppliers are increasingly demanding transparency regarding environmental impact. Businesses may need to provide detailed information about their carbon footprint to meet customer expectations and comply with supply chain requirements. This transparency helps build trust and demonstrates a company’s commitment to sustainability.
Suppliers also play a crucial role, as they may require carbon footprint data to ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards. By measuring and reporting carbon emissions accurately, companies can strengthen relationships with customers and suppliers, ensuring alignment with sustainability goals.
Interest of Investors and Cost Saving
Investors are increasingly considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors when making investment decisions. Companies that measure and report their carbon footprint can attract investment by demonstrating their commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices.
The global Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) database collects and shares carbon footprint data, enabling investors to make informed decisions. Additionally, identifying energy-intensive activities through carbon footprint measurement can lead to cost savings by reducing energy consumption and other costs by optimizing resource use. Companies can achieve financial benefits while minimizing their environmental impact by implementing energy-efficient practices and sustainable solutions.
Preparing for Carbon Footprint Calculation
Gathering data and information
Accurate carbon footprint calculation requires comprehensive data collection on energy consumption, transportation, and other activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Start by identifying emission sources within your organization and defining the boundaries of your calculation.
Collect data from utility bills, fuel consumption records, travel logs, and waste management reports. Various tools and services can assist in this process, providing businesses with the necessary resources to calculate their carbon footprint effectively. Ensuring accurate and detailed data collection is crucial for reliable carbon footprint assessment and subsequent reduction strategies.
Identifying Emission Sources and Boundaries
Identifying direct and indirect emission sources is a critical step in carbon footprint calculation. Direct emissions (Scope 1) include on-site fuel combustion and company-owned vehicle emissions, while indirect emissions (Scope 2 and 3) cover purchased electricity and activities within the value chain. Defining the boundaries of your carbon footprint calculation involves determining which activities and processes to include, ensuring a comprehensive assessment.
This process helps organizations understand their total emissions, enabling them to target reduction efforts where they will have the most significant impact.
Choosing a Calculation Method
Selecting the appropriate calculation method is essential for accurate carbon footprint measurement. The Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHGP) is a widely accepted standard that provides guidelines for calculating and reporting greenhouse gas emissions. Businesses can use carbon footprint calculators, specialized software, or consulting services to assist with the calculation.
The method chosen should align with the organization’s size, complexity, and specific needs. The World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development developed the GHGP, establishing a global standard for carbon footprint measurement and ensuring consistency and accuracy in reporting.
Calculating Your Carbon Footprint
Consumption-based emission accounting
Consumption-based emission accounting traces the impacts of demand for goods and services along the global supply chain to the end consumer. Also known as consumption-based carbon accounting, this method is based on input-output analysis, providing a detailed view of emissions generated by consumption activities.
This approach helps identify the carbon footprint of products and services throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal. By understanding the consumption-based emissions, organizations can develop strategies to reduce their overall environmental impact and promote sustainable consumption patterns.
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and Combination Methods
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) assesses all environmental impacts associated with the life cycle of a product, process, or service, including water pollution, air pollution, ecotoxicity, and similar types of pollution. LCA provides a comprehensive evaluation of the carbon footprint, considering all stages from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Combining LCA with other methods, such as consumption-based accounting, offers a holistic view of environmental impacts. Carbon footprints are typically expressed in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e), allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of other greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide.
Using Carbon Footprint Calculators and Tools
Utilizing online carbon footprint calculators and tools can simplify the process of measuring emissions. These tools provide estimates based on user inputs, such as energy consumption, travel data, and waste generation.
Specialized software and consulting services can offer more detailed and accurate assessments for businesses with complex operations. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the calculation method is crucial for developing effective carbon reduction strategies. By using these tools, individuals and organizations can track their progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to reduce their carbon footprint.
Reducing Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Strategies for businesses and individuals
Implementing energy-efficient practices and renewable energy sources is a key strategy for reducing carbon emissions. Businesses and individuals can reduce energy consumption by using energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and adopting sustainable transportation methods. Reducing waste and increasing recycling efforts also contribute to lower emissions.
Encouraging sustainable commuting practices, such as carpooling, biking, or using public transportation, further reduces carbon footprints. By adopting these strategies, organizations and individuals can significantly lower their environmental impact and promote sustainability.
Biggest Causes of Carbon Emissions and How to Address Them
Identifying the largest sources of greenhouse gas emissions is essential for effective reduction strategies. Major contributors include energy production, transportation, and industrial processes. Developing strategies to reduce energy consumption and emissions involves adopting renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and implementing waste reduction measures.
Addressing these key areas can lead to significant reductions in carbon emissions. Implementing measures such as energy audits, process optimization, and waste management can help organizations large companies, and individuals minimize their carbon footprint and contribute to climate change mitigation.
Climate Change Mitigation and Industry’s Role
Industries play a crucial role in climate change mitigation by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices. Implementing measures to reduce emissions, such as adopting clean energy technologies, improving energy efficiency, and minimizing waste, is essential for mitigating climate change.
Encouraging sustainable practices throughout the supply chain, including suppliers and partners, further enhances environmental impact. Industries must take responsibility for their emissions and actively contribute to global efforts to combat climate change. By prioritizing sustainability, industries can drive positive to tackle climate change and support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Implementing a Carbon Reduction Plan

Developing a reduction strategy and roadmap
Developing a robust carbon reduction strategy involves setting clear goals and targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Creating a roadmap for achieving these goals includes identifying key stakeholders, defining roles, and outlining specific actions to be taken.
Setting measurable and realistic targets ensures accountability and progress tracking. Engaging stakeholders in the planning process fosters collaboration and commitment to achieving the reduction goals. By developing a comprehensive strategy and roadmap, organizations can effectively reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Engaging Stakeholders and Communicating Progress
Effective communication is vital for the success of a carbon reduction plan. Communicating the plan to stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and suppliers, ensures transparency and accountability. Engaging employees and encouraging their participation in sustainability initiatives fosters a culture of environmental responsibility.
Regularly reporting progress and achievements to stakeholders builds trust and demonstrates commitment to carbon reduction goals. By maintaining open communication and involving stakeholders in the process, organizations can further carbon trust and drive collective action towards sustainability.
Monitoring and Reporting Carbon Emissions
Establishing a system for monitoring and tracking greenhouse gas emissions is essential for measuring progress and identifying areas for improvement. Regularly reporting emissions to stakeholders provides transparency and accountability.
Using data to identify trends and opportunities for further reduction helps refine the carbon reduction strategy. Implementing monitoring and reporting systems ensures that organizations can track their emissions accurately, report on their progress, and make informed decisions to enhance their sustainability efforts.
Overcoming Challenges in Carbon Footprint Measurement
Addressing data quality and uncertainty
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data is crucial for effective carbon footprint measurement. Addressing data quality involves validating data sources, verifying data accuracy, and addressing any uncertainties or variability in data.
Using sensitivity analysis to test assumptions and identify potential errors helps improve the reliability of the carbon footprint calculation. By focusing on data quality and addressing uncertainties, organizations can ensure accurate measurement and reporting of their greenhouse gas emissions.
Managing Scope and Boundaries
Defining the scope and boundaries of the carbon footprint calculation is essential for comprehensive and accurate measurement. Ensuring that the scope includes all relevant emission sources and activities provides a complete view of the organization’s environmental impact.
Considering the use of sensitivity analysis to test assumptions and refine the scope helps improve the accuracy of the calculation. By clearly defining and managing the scope and boundaries, organizations can ensure that their carbon footprint measurement reflects their total emissions accurately.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are key principles in carbon footprint measurement. Providing clear and concise information to stakeholders ensures that the carbon footprint calculation is transparent and credible. Encouraging stakeholder engagement and participation in the measurement process fosters a culture of accountability and environmental responsibility. By ensuring transparency and accountability, organizations can build trust with stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Best Practices for Accurate Carbon Footprint Measurement
Emerging trends and concepts in carbon footprint measurement
Staying up-to-date with emerging trends and concepts in carbon footprint measurement is essential for continuous improvement. Considering the use of new technologies and methods, such as advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence, can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of carbon footprint calculations.
Encouraging innovation and continuous improvement ensures that organizations remain at the forefront of sustainability practices and can effectively reduce their greenhouse gas emissions.
Integrating Carbon Footprint into Business Strategy and Operations
Incorporating carbon footprint considerations into business strategy and operations is crucial for achieving long-term sustainability goals. Encouraging a culture of sustainability involves integrating carbon footprint measurement into decision-making processes and operational practices.
Ensuring that carbon footprint is considered in product design, supply chain management, and overall business strategy helps organizations align their activities with environmental goals and reduce their carbon emissions.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Promoting a culture of continuous improvement and innovation is key to effective carbon footprint management. Identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes based on data and feedback helps organizations refine their strategies and achieve better environmental outcomes. Staying informed about the latest research and developments in carbon footprint measurement ensures that organizations can adopt best practices and remain competitive in their sustainability efforts.
Conclusion
Recap of key takeaways
Measuring your carbon footprint is essential for understanding and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Accurate carbon footprint measurement requires careful planning, data collection, and execution. Implementing a carbon reduction plan with clear goals, stakeholder engagement, and regular carbon monitoring, can help achieve sustainability objectives.
